In the pharmaceutical sector, deviation reports and corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) are crucial instruments for locating, examining, and addressing quality-related problems. These reports are essential for preserving adherence to legal requirements and guaranteeing ongoing process development. Nevertheless, poor quality and missing information can make CAPA and Deviation Reports less useful. To improve the calibre and effectiveness of these reports, a few crucial aspects need to be taken into account. This article will discuss seven important factors that should be taken into account to raise the calibre of CAPA and Deviation Reports, which will ultimately result in greater quality control and compliance in the pharmaceutical sector as a whole.
Here are some key topics to focus on improving the quality of your deviation/ investigation reports
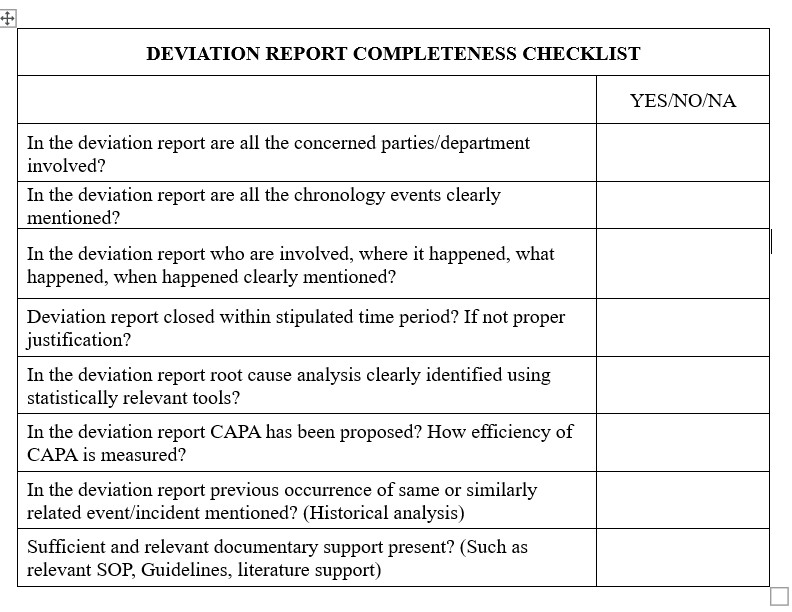
1. Accessibility: The investigation/deviation report should be easily accessible and effectively perceived by all parties well; after the event and the investigation. Deviation report must provide scientific proof and a systematic methodology that takes in to account the incident findings.
2. Due time: A well researched deviation investigation should be completed within stipulated time period. (In most organizations typically within 30 days)
Contents in the deviation investigation should include the following components:
3. Chronology of the deviation: Include the who, where, what, when details in this section. Be explicit information such as exact date and accurate data. Give exact information and facts in chronological order, which include data or observations prior to, during and or after the event. Provide appropriate data as to how the incident was controlled and additionally at the situation time.
4. Provide documentary evidence for Batches affected and criteria of selection: Organization should have well defined SOP for selection of Batches, SOP must be very clear how if any potential risk was addressed immediately and that the criteria for identification and control of the affected material.
5. Root-Cause Investigation: This is the part to exhibit that a deliberate methodology was taken to explore the most appropriate true root cause of the issue. Often Root Cause Investigation is investigated by various Tools: 5Why’s, Fish-Bone Analysis and all tools should be scientifically applied
6. CAPA Efficiency measurement: Efficiency of deviation and CAPA should be investigated in timely manner. The assessment and resulting conclusions must be objective and scientific based. Identification of appropriate corrective and preventative actions should be completed based on the root cause investigation section and should address all root causes identified.
7. Historical Analysis: Appropriate documentary evidence should be provided to record deviations and CAPA’s. Yearly data is curate and statistical analysis is done. Any re-occurrence quality issues should be investigated and efficiency CAPS or deviation should be measured.
Now that you know this:- hopefully you are in position to answer the Assignment(s)
Is CAPA efficiency being adequately monitored by your QA/QC department? How are they quantified?
Are OOT/OOS/OOC/Incidents routinely monitored by your QA department? Do they necessitate conversations and insights with the QC and analytical departments?
Does your QA/QC department thoroughly examine root cause analysis using techniques like 5-whys? Does the staff have enough background knowledge to look into root cause analysis?