Any data or observations that depart from the established or anticipated trend are referred to as out-of-trend results. These outcomes can be seen in a number of disciplines, including quality assurance, and scientific research. When outcomes are shown to be out of trend, it’s critical to assess and comprehend the causes. The importance of assessing out-of-trend findings, their possible causes and prevention strategies will all be covered in this article. We can enhance the validity and consistency of our trends and make well-informed selections by comprehending the ramifications of out-of-trend results. Further, there is a need for efficient and practical statistical approach to identify OOT results when a batch is not behaving as expected.
Methodology
- A minimum of 25 – 30 batches data shall be compiled for fixing the Trend range.
- Results that shall be obtained from the 25 batches tabulated, average value,
minimum and maximum values are noted. - Standard deviation will be calculated for these batches. Excel spread sheet
shall be used for Standard deviation calculation. - Maximum and minimum limits shall be taken as the Trend range for upper and lower limits by using 3 sigma method.
- Any value that shall be out of this range will be considered as Out of Trend
(OOT) value or Outlier value. - Wherever specification has only Not more than, then only Maximum limit for
trend can be considered. Minimum limit should be excluded. - Wherever specification has range then both the Maximum and Minimum limits
for trend should be considered.
Key Questions:
Numerous challenges exist that a company must overcome to implement an OOT procedure for commercial batches…
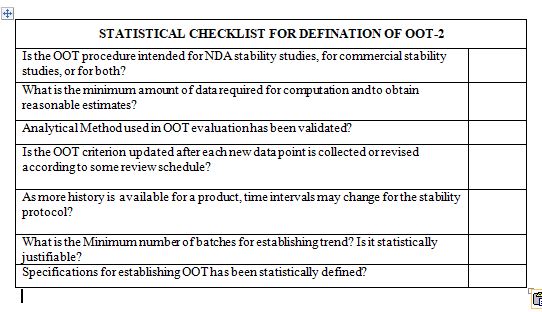
What statistical approaches are used to determine OOT criterion?
What are the minimum data requirements? What evaluation is performed if the minimum data requirement is not met?
What data should be used to update limits?
The investigation requirements (i.e., who is responsible, what is the timeline, how is it documented, who should be notified must be clearly defined.
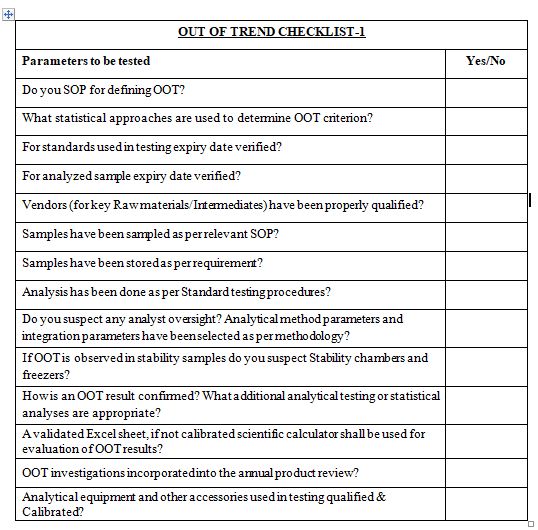
How is an OOT result confirmed? What additional analytical testing or statistical analyses are appropriate?
How are OOT investigations incorporated into the annual product review?
After reading this blog, we hope you can understand the importance of computer system validation and properly use the proposed checklist and improve on it further.
Now that you know this:- hopefully you are in position to answer the Assignment(s)
How does one verify an OOT result? Which extra statistical analysis or analytical testing is necessary?
What role do OOT investigations play in the yearly product review?
What minimal amounts of data required for establishing OOT? If the minimal amount of data is not met, what assessment is carried out?