Out-of-trend identification and removal is a critical aspect in maintaining the quality and reliability of any manufacturing process. As trends and patterns in data can significantly impact the product’s performance and consistency, it is essential to detect and eliminate any out-of-trend data points. In recent years, various methods have been developed to address this issue, including regression analysis and closed-loop approach methods. These techniques offer efficient and accurate ways to detect and remove outliers and trends in data, ensuring the production of high-quality products. In this article, we will delve into the details of these two approaches and explore their application in out-of-trend identification and removal.
The following are typical historical approaches to OOT identification and removal, though they are not recommended approaches. They are not considered to be statistically sound procedures for OOT identification and removal. The difference between consecutive results is outside of half the difference between the prior result and the specification
The result is outside ±5% of initial result
The result is outside ±3% of previous result
The result is outside ±5% of the mean of all previous results.
Closed-Loop Approach to OOT identification and removal
A best-practice approach to OOT determination and removal is to see it as a part of a closed-loop control system during stability monitoring and expiry prediction. The five steps to a closed loop system for OOT are:
- Addition of new time points and data
- OOT identification
- OOT determination and point removal where warranted
- OOT verification and evaluation of OOT influence
- Stability and performance prediction.
Addition of New Time Points and Data, Closed Loop
As each new time point is added to the stability analysis, the time point should be checked for OOT potential. If they are within the criteria for OOT identification, then rates of change, expiry, etc. are determined. OOT identification, determination, and verification are used if new time points appear to be suspect.

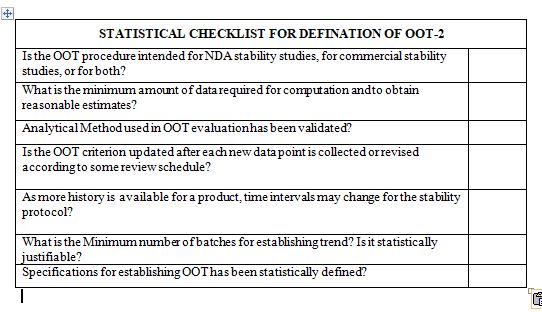
Now that you know this:- hopefully you are in position to answer the Assignment(s)
- Selection of valid and reliable statistical approaches to determine OOT criterion?
- Establishing and Evaluation of OOT: Minimum data requirements? Data requirements to be used to update upper and lower limits? Is it justified?
- The execution and accountability necessities (i.e., who is accountable? What is timeframe, clear Standard operating procedures (SOP) shall be defined, and responsibility must be clearly defined?
- If OOT result is obtained as per defined SOP, further analytical testing requirements to confirm and establish the results?
- Had the OOT investigations documented into the annual product review?